AngularJS provides great support for implemeting validations in Forms.
Validation is performed by States properties and Validators directives.
There are four States in AngularJS Forms.
- $invalid : This state describes that form is in invalid state.
- $valid : This state describes that form is in valid state.
- $dirty :This state describes that form is in dirty state means any one input control value has changed by user.
- $error : This is a javascript object whose properties ‘required’, ‘minlength’, ‘maxlength’ has been set to true when any matching validation is true.
There are main four AngularJS Validators directives.
- ng-required : Set input control required and set the ‘required’ attribute of $error if input control is empty.
- ng-minlength : Set minimum length of input field and set the ‘minlength’ attribute of $error to true if input control does not satisfy the ng-minlength validation.
- ng-maxlength : Set maximum length of input field and set the ‘maxlength’ attribute of $error to true if input control does not satisfy the ng-maxlength validation.
- ng-pattern : Match the reqular expression and set the ‘pattern’ attribute of $error to true if input control does not satisfy the ng-pattern validation.
In addition we used three additional directives:
- ng-model : Bind input controls to AngularJS controller objects.
- ng-disabled : Disabled the associated element while condition is satisfied.
- ng-show : Show the associated element while condition is satisfied else hide the element.
AngularJS Form Validation Example
<html>
<head>
<title>AngularJS Form Validation Example</title>
</head>
<body ng-app="testApp" ng-controller="mainCtrl">
<form name="myForm" ng-submit="submit()" >
<p>
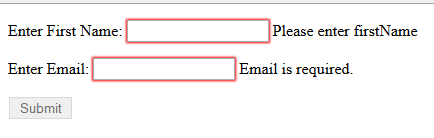
Enter First Name: <input name="firstName" type="textbox" ng-model="user.firstName" ng-required="true" ng-minlength="4" ng-maxlength="8" />
<span ng-show="myForm.firstName.$error.required">
Please enter firstName
</span>
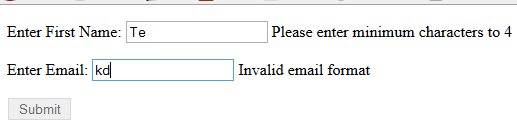
<span ng-show="myForm.firstName.$error.minlength">
Please enter minimum characters to 4
</span>
<span ng-show="myForm.firstName.$error.maxlength">
Please enter maximum characters to 8
</span>
</p>
<p>
Enter Email: <input name="email" type="textbox" ng-model="user.email" ng-required="true" ng-pattern="/^\w+@[a-zA-Z_]+?\.[a-zA-Z]{2,3}$/" />
<span ng-show="myForm.email.$error.required">
Email is required.
</span>
<span ng-show="myForm.email.$error.pattern">
Invalid email format
</span>
</p>
<p>
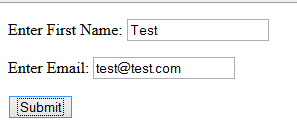
<input type="submit" value="Submit" ng-disabled="myForm.$invalid" />
</p>
</form>
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.3.8/angular.min.js" ></script>
<script>
var app = angular.module('testApp', []);
app.controller('mainCtrl', ['$scope', function($scope){
$scope.user = { firstName: '', email: ''};
$scope.submit = function()
{
console.log('FirstName: ' + $scope.user.firstName);
console.log('Email: ' + $scope.user.email);
};
}]);
</script>
</body>
</html>Result:
- Line 9 defines an input control which has ng-model, ng-required, ng-minlength, ng-maxlength directives.
- Line 10,13,16 defines a ng-show directives which only visible when its associated bind property is set to true.
- Line 11, 14, 17 shows error messages which only visible when ng-show directive is set to true.
- Line 21 shows an example of ng-pattern directive which validate the input control for valid email.
- LIne 22, 25 span will only be visible when bind properties is set to true.
- Line 30 defines an input submit button with ng-disabled directive which disable the submit button until the form is in valid state.
- Line 36 to 46 defines an angular app and controller which show the user information in console when user submit the form.